How to Secure Your Google Account from Hackers: The Ultimate Expert Guide to Digital Fortress
In today’s hyper-connected world, your Google account isn't just an email address; it's the central nervous system of your digital life. From sensitive emails and personal photos to financial information and access to countless online services, a compromised Google account can lead to devastating consequences. As a professional SEO expert deeply entrenched in the realm of online security, I understand the critical importance of safeguarding this digital hub. This comprehensive guide will arm you with the knowledge and actionable strategies to build an impenetrable fortress around your Google account, ensuring your online safety and protecting your invaluable data from insidious cybersecurity threats.
The Foundation of Impregnable Security: Crafting and Managing Strong Passwords
While often underestimated, your password remains the first line of defense against unauthorized access. A weak password is an open invitation for hackers. It's not enough to simply have a password; it must be a formidable barrier. Think of it as the ultimate lock on your digital vault.
Characteristics of a Truly Strong Password:
- Length is King: Aim for at least 12-16 characters, but longer is always better. Every additional character exponentially increases the complexity.
- Complexity is Queen: Combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters (e.g., !@#$%^&). Avoid predictable patterns.
- Uniqueness is Non-Negotiable: Never reuse passwords across different accounts. If one service is breached, all accounts using that same password become vulnerable. This is a common pitfall in account security.
- Forget Predictability: Avoid personal information like birth dates, pet names, or common dictionary words. Hackers often use automated "brute-force" attacks or dictionary attacks.
Leveraging Password Managers for Superior Security:
Memorizing dozens of unique, complex passwords is impractical. This is where a password manager becomes an indispensable tool for robust data protection. These encrypted vaults store all your login credentials securely, allowing you to use a single, strong master password to access them. Popular choices like LastPass, 1Password, Bitwarden, or Dashlane generate, store, and auto-fill complex passwords, significantly enhancing your digital privacy. They also alert you to compromised passwords and help you update them regularly. Learn more about choosing the best password manager for your needs.
The Unbreakable Shield: Activating Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Even the strongest password can be compromised through sophisticated phishing attacks or data breaches. This is why two-factor authentication (2FA), also known as two-step verification, is absolutely critical. It adds a second layer of security, requiring not just something you know (your password) but also something you have (your phone or a security key).
Why 2FA is Your Ultimate Defense:
If a hacker manages to steal your password, they still cannot access your account without that second factor. This makes unauthorized access exponentially more difficult. Google offers several 2FA options, each with varying levels of security.
Setting Up 2FA on Your Google Account:
- Access Google Security Settings: Go to myaccount.google.com/security.
- Navigate to "How you sign in to Google": Find "2-Step Verification" and click "Get started."
- Choose Your Second Step:
- Google Prompt (Recommended for ease of use): Your phone receives a notification asking if you're trying to sign in. Simply tap "Yes." This is often the most convenient and secure option for most users.
- Authenticator App (More secure than SMS): Apps like Google Authenticator or Authy generate time-sensitive codes. These codes work even if you don't have cell service.
- Security Key (Most Secure): A small physical device (like a YubiKey) that plugs into your computer's USB port or connects via Bluetooth/NFC. It's resistant to sophisticated phishing attempts. Consider this if you handle highly sensitive information.
- Backup Codes: Generate and print a set of one-time use codes. Keep them in a safe, offline location. These are crucial if you lose your phone or security key.
- SMS Verification (Least Secure 2FA option): While better than no 2FA, SMS codes can be intercepted through SIM-swapping attacks. Use this only if other options aren't feasible.
- Set Up Backup Methods: Always set up at least two 2FA methods, including backup codes and a recovery phone/email, to ensure you never get locked out.
Proactive Defense: Regularly Utilizing Google's Security Checkup
Google provides a powerful, free tool to help you monitor and enhance your account's security posture: the Google Security Checkup. Regularly performing this checkup is akin to a digital health audit, identifying potential vulnerabilities before they become problems.
What the Google Security Checkup Reviews:
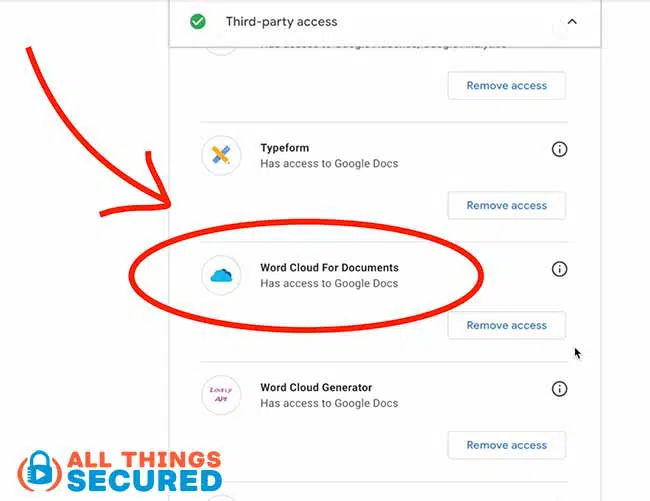
- Third-Party Access: It lists all apps and services that have permission to access your Google account data. Revoke access for any apps you no longer use or don't recognize. This is a critical step in preventing unauthorized access.
- Connected Devices: See all devices currently signed into your Google account. If you spot an unfamiliar device, sign it out immediately. This is vital for tracking suspicious activity alerts.
- Recent Security Events: Review a log of recent sign-ins, password changes, and other security-related activities. This helps you quickly identify any unauthorized actions.
- Recovery Information: Ensures your recovery phone number and email address are up-to-date. This is paramount for account recovery if you ever lose access.
- 2-Step Verification Status: Confirms whether 2FA is enabled and what methods are active.
Make it a habit to run the Google Security Checkup tool at least once a month. It's a quick, actionable step that significantly boosts your account security.
Safeguarding Your Recovery Options and Trusted Contacts
Even with the best security measures, situations arise where you might need to recover your account – perhaps you forgot your password, lost your phone, or Google detects unusual activity. Having accurate and up-to-date recovery options is your safety net.
- Recovery Phone Number: Ensure this number is current and that you have access to it. Google uses it to send verification codes during account recovery.
- Recovery Email Address: Provide an alternative email address, preferably one from a different provider, that you can access even if your Google account is locked.
- Trusted Contacts (Account Recovery): Google allows you to designate trusted contacts who can help you regain access to your account if you get locked out. They receive codes from Google that you can use to verify your identity. This is a powerful feature for extreme cases of lockout.
Regularly verify that these recovery details are accurate. A forgotten or outdated recovery option can turn a minor inconvenience into a permanent lockout.
Recognizing and Evading Phishing Scams and Social Engineering
The human element remains the weakest link in any security chain. Hackers frequently exploit this through sophisticated phishing attacks and social engineering tactics. These attempts try to trick you into revealing your login credentials or other sensitive information.
Common Red Flags of Phishing Attempts:
- Suspicious Sender: The email address doesn't match the legitimate sender (e.g., "gooogle.com" instead of "google.com").
- Urgent or Threatening Language: Phrases like "Your account will be suspended immediately!" or "Action required now!" are designed to create panic and bypass critical thinking.
- Generic Greetings: Instead of addressing you by name, they might use "Dear User" or "Valued Customer."
- Poor Grammar and Spelling: Professional organizations typically have well-proofread communications.
- Links to Unknown Websites: Hover over links without clicking to see the actual URL. If it doesn't lead to a legitimate Google domain (e.g., accounts.google.com), do not click.
- Requests for Personal Information: Google will never ask for your password, credit card number, or other sensitive details via email.
Practical Advice to Avoid Phishing:
- Verify Before You Click: If an email seems suspicious, open your browser and navigate directly to the official Google website or service (e.g., Gmail.com, Drive.google.com) instead of clicking the link in the email.
- Report Phishing: If you receive a phishing email, report it to Google by clicking the "Report phishing" or "Report spam" button in Gmail. This helps Google improve its filters and protect other users.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest phishing techniques. Knowledge is your best defense against these evolving cybersecurity threats.
- Browser Extensions: Consider using browser extensions that warn you about malicious websites, though these should not be your sole defense.
Managing Third-Party App Access and Permissions
Many legitimate apps and services request permission to access parts of your Google account data (e.g., your calendar, contacts, or Drive files). While convenient, granting excessive or unnecessary permissions can create security vulnerabilities. A rogue app or a compromised third-party service could inadvertently expose your data.
- Regularly Review Permissions: Navigate to your Google Account Permissions page.
- Revoke Unnecessary Access: For any app you no longer use, don't recognize, or whose access seems too broad for its function, revoke its permissions immediately. This is a crucial step in maintaining your digital privacy.
- Be Selective: Before granting access to a new app, carefully read what permissions it requests. If it asks for more than it reasonably needs, reconsider using it.
Staying Vigilant: Monitoring Account Activity and Alerts
Google actively monitors your account for unusual activity and will often alert you to potential security issues. Paying attention to these alerts is a key component of proactive account security.
- Google Security Alerts: If Google detects a suspicious sign-in attempt, a new device logging in, or a password change from an unusual location, it will send you an email or a notification on your phone. Do not ignore these. Act immediately to verify the activity or secure your account.
- Reviewing Activity Logs: You can manually review your recent activity by visiting Google's Security Events page. This shows a chronological list of sign-ins, password changes, and other security-related actions. If you spot anything unfamiliar, take immediate action.
- Linked Accounts: Be aware of any other services that use "Sign in with Google." If your Google account is compromised, these linked accounts could also be at risk.
If you suspect unauthorized access, change your Google password immediately and run a full Security Checkup.
Advanced Protection Program: For High-Risk Individuals
For journalists, activists, government officials, or anyone at high risk of targeted online attacks, Google offers the Advanced Protection Program. This program provides Google's strongest security measures, including:
- Mandatory Security Keys: Requires the use of physical security keys for sign-in, which are highly resistant to phishing.
- Strict Verification: Requires additional steps for account recovery, making it much harder for attackers to gain access even with stolen credentials.
- Limited Third-Party Access: Automatically blocks most non-Google apps from accessing your data.
While not for everyone, it offers an unparalleled level of data protection for those who need it most. Explore if Google's Advanced Protection Program is right for you.
What to Do If Your Google Account Is Compromised
Despite all precautions, sometimes the worst happens. Knowing what to do immediately can mitigate damage and help you regain control.
- Change Your Password Immediately: If you can still access your account, change your password to a new, strong, and unique one.
- Run a Security Checkup: Use Google's Security Checkup tool to review connected devices, third-party app access, and recent security events. Remove anything suspicious.
- Review and Secure Recovery Options: Ensure your recovery phone and email are correct and secure.
- Check for Forwarding Rules: In Gmail, check your settings for any malicious forwarding rules that might be sending your emails to an attacker.
- Report to Google: If you're locked out, use Google's account recovery process. Be prepared to answer questions about your account and provide verification. The more accurate information you can provide, the better your chances of recovery.
- Inform Your Contacts: Warn friends and family that your account was compromised, as attackers often use hacked accounts to send phishing emails to contacts.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I review my Google security settings?
As a best practice for online safety, you should aim to conduct a full Google Security Checkup at least once every three months, or immediately if you notice any unusual activity or receive a security alert. Regularly reviewing connected devices, third-party app access, and recovery options ensures your account security remains robust against evolving cybersecurity threats.
Is SMS 2FA secure enough for my Google account?
While SMS-based two-factor authentication is significantly better than having no 2FA at all, it is generally considered less secure than other methods like authenticator apps or security keys. SMS codes can be vulnerable to "SIM-swapping" attacks, where hackers trick your mobile carrier into porting your phone number to their device. For optimal data protection, Google Prompt, authenticator apps, or physical security keys are highly recommended.
What is a security key and why is it considered the most secure 2FA option?
A security key is a small, physical USB, Bluetooth, or NFC device that you use to verify your identity when signing into your Google account. It's considered the strongest form of two-step verification because it's virtually immune to phishing attacks. Unlike codes sent via SMS or generated by an app, a security key uses cryptographic verification, ensuring that you are indeed interacting with the legitimate Google site and not a fraudulent one. This provides unparalleled digital privacy and defense against sophisticated attacks.
Can a password manager be hacked?
While no system is 100% immune, reputable password managers employ strong encryption and sophisticated security protocols, making them extremely difficult to hack. The primary vulnerability usually lies with the user's master password or if the user falls victim to a phishing scam that tricks them into revealing it. As long as you use a unique, strong master password and enable 2FA on your password manager itself, your stored credentials are far more secure than if you were to reuse or write down passwords. They are a cornerstone of modern password management and overall account security.
How do I report a suspicious email claiming to be from Google?
If you receive an email that looks like it's from Google but seems suspicious (e.g., asking for your password, containing unusual links, or threatening account closure), do not click on any links or download attachments. Instead, open your Gmail, select the suspicious email, and click the "Report phishing" or "Report spam" option (usually found in the three-dot menu next to the reply button). Reporting these emails helps Google's systems learn and protect other users from similar phishing attacks.

0 Komentar