How to Secure Your Zoom Meetings: A Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Cyber Attacks and Zoom Bombing
In today's hyper-connected world, Zoom meetings have become an indispensable tool for work, education, and social interaction. However, the convenience of virtual collaboration comes with inherent risks, particularly the threat of unauthorized access, disruptions, and privacy breaches. This comprehensive guide, crafted by an SEO expert, will equip you with the essential knowledge and actionable strategies to safeguard your virtual calls, ensuring your discussions remain private, productive, and free from the specter of Zoom bombing or other malicious cyber threats. Protect your sensitive information and maintain control over your online environment by implementing these robust online meeting security protocols.
Understanding the Threat Landscape: Why Zoom Security Matters
The rapid adoption of video conferencing platforms like Zoom has unfortunately also attracted the attention of malicious actors. From pranksters disrupting a class to sophisticated cybercriminals attempting to exfiltrate sensitive corporate data, the range of threats is broad. Zoom bombing, a term coined during the pandemic, refers to the act of uninvited individuals gatecrashing and disrupting a meeting, often by sharing inappropriate content or verbally harassing participants. Beyond these disruptions, there are more insidious risks, such as the potential for malware distribution, phishing attempts through shared links, or the unauthorized recording and distribution of private conversations. Implementing robust video conferencing best practices is no longer optional; it's a critical component of modern digital hygiene.
The core issue often stems from default settings that prioritize ease of use over stringent security. Many users, unaware of the potential vulnerabilities, fail to configure their meetings properly, leaving open doors for exploitation. Our focus here is to close those doors, one setting at a time, transforming your Zoom sessions into fortified digital spaces. Understanding the common attack vectors, such as guessing meeting IDs, exploiting shared links, or simply entering unprotected rooms, is the first step toward building an impenetrable defense for your virtual collaboration safety.
Pre-Meeting Security Protocols: Fortifying Your Foundations
The most effective security measures are often those implemented before your meeting even begins. Proactive steps can drastically reduce the likelihood of a security incident. These foundational elements are crucial for comprehensive Zoom meeting protection.
1. Account Security: Your First Line of Defense
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This is non-negotiable. 2FA adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second verification method (like a code from your phone) in addition to your password. Even if your password is compromised, an attacker cannot access your account without your second factor.
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Never reuse passwords across different services. Employ a complex password combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. A password manager can greatly assist with this.
- Regularly Update Your Zoom Client: Zoom frequently releases updates that include crucial security patches and new features. Always ensure your desktop client and mobile app are running the latest version to benefit from the most current protections against known vulnerabilities. Neglecting updates leaves you exposed to recently discovered cyber threats.
2. Scheduling Settings: Building a Secure Meeting from the Ground Up
When you schedule a meeting, Zoom offers a suite of security options that are often overlooked. Leveraging these effectively is paramount.
- Require a Passcode for All Meetings: This is perhaps the simplest yet most effective deterrent against unauthorized access. Ensure a strong, unique passcode is generated for each meeting. Communicate this passcode only to intended participants.
- Enable the Waiting Room Feature: The Waiting Room is your virtual bouncer. It allows the host to admit participants individually or all at once. This is incredibly effective at preventing Zoom bombing because no one can join the main meeting until you explicitly allow them. It gives you control over who enters your space.
- Disable "Join Before Host": Unless absolutely necessary for your specific use case, disable this option. When enabled, participants can join the meeting before the host, potentially starting conversations or even sharing content unsupervised. Keeping it disabled ensures that you, as the host, are always the first one in the room, setting the tone and controlling access.
- Use Unique Meeting IDs: For sensitive meetings, avoid using your Personal Meeting ID (PMI). PMIs are static and, if exposed, can be exploited repeatedly. Instead, generate a unique, random meeting ID for each session.
- Limit Screen Sharing: Under "Advanced Sharing Options," restrict who can share their screen to "Host Only." This prevents participants from unexpectedly sharing inappropriate content, a common tactic in Zoom bombing incidents.
- Consider Requiring Authentication: For highly sensitive meetings, you can configure Zoom to require participants to be signed in to Zoom and/or to be part of a specific domain. This adds a powerful layer of verification, ensuring only authenticated users can join.
In-Meeting Security Measures: Maintaining Control During Your Session
Even with robust pre-meeting settings, active management during the session is vital. Zoom provides powerful host controls that allow you to react swiftly to any emerging threats or disruptions.
1. Mastering Host Controls: Your Virtual Toolkit
Once your meeting has started, familiarizing yourself with the security options available in the meeting toolbar is critical. These controls are usually found under the "Security" icon.
- Lock the Meeting: Once all expected participants have joined, you can "Lock Meeting" from the Security icon. This prevents anyone else from joining, even if they have the meeting ID and passcode. It's an excellent way to secure your session once attendance is confirmed.
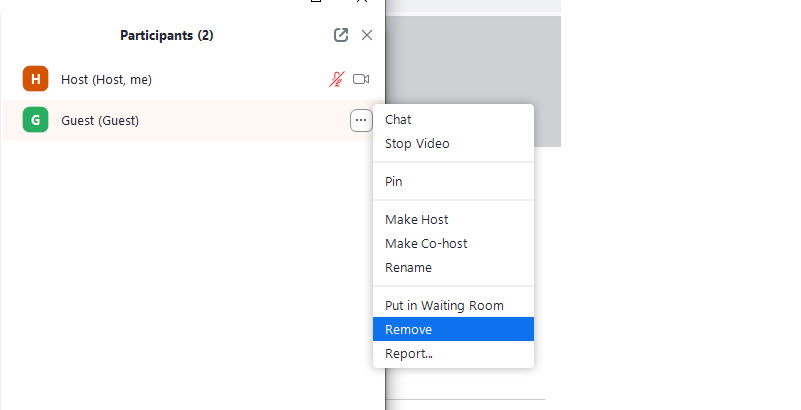
- Remove Participants: If an uninvited guest slips through or a participant becomes disruptive, you can easily remove them. Hover over their name in the participant list, click "More," and then "Remove." Once removed, they cannot rejoin the meeting.
- Mute Participants: For large meetings or to prevent background noise, you can mute individual participants or all participants at once. You can also prevent participants from unmuting themselves, giving you complete audio control. This is particularly useful in educational settings or webinars.
- Disable Participant Chat: If the chat function is being misused, or if you simply don't need it, you can disable it entirely, or restrict it to "Host Only" or "Host and Co-hosts." This prevents spam, inappropriate messages, or the sharing of malicious links.
- Suspend Participant Activities: In extreme cases of disruption, Zoom offers a "Suspend Participant Activities" feature. This instantly stops all video, audio, and screen sharing, mutes all participants, and locks the meeting, allowing the host to address the issue without further disruption.
2. Managing Content Sharing and Collaboration
Screen sharing and file transfer capabilities, while useful, can also be vectors for attack if not managed properly.
- Control Screen Sharing Permissions: As mentioned, setting screen sharing to "Host Only" is the safest default. If participants need to share, you can temporarily grant them permission or make them a co-host and then revoke it. This proactive approach to screen sharing security prevents unauthorized content from appearing.
- Disable File Transfer: If your meeting doesn't require file sharing through Zoom's chat, disable this feature. This prevents participants from sending potentially malicious files or unwanted content.
- Control Annotation: Annotation tools can be used to deface shared screens. If you're sharing your screen, you can disable participant annotation to prevent unwanted drawings or text on your presentation.
3. Recording and Data Privacy
Recording meetings can be beneficial, but it also introduces data privacy considerations.
- Obtain Consent for Recording: Always inform participants if the meeting is being recorded. In many jurisdictions, this is a legal requirement. Zoom has built-in notifications, but verbal confirmation is good practice.
- Secure Cloud Recordings: If you record to the Zoom cloud, ensure you understand and utilize the security settings for those recordings. You can add passcodes to cloud recordings, set expiration dates, and restrict viewing to authenticated users. Avoid sharing direct links to recordings publicly.
- Understand End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): While Zoom offers E2EE, it comes with certain limitations (e.g., disables some features like cloud recording, live transcription). For most standard meetings, Zoom's enhanced encryption (AES 256-bit GCM) is robust. For highly sensitive discussions requiring true E2EE, be aware of the feature trade-offs. This level of end-to-end encryption is typically reserved for the most private conversations.
Advanced Security Configurations & Tips for Power Users
Beyond the basic settings, there are several advanced configurations and expert tips that can further enhance your online meeting security posture.
1. Utilizing Zoom's Web Portal Settings
Many of Zoom's most powerful security settings are configured via the web portal (zoom.us/profile/setting). These settings apply globally to all your scheduled meetings unless overridden at the individual meeting level.
- Review Account-Level Security Settings: Regularly audit your account settings. Ensure that features like "Require a passcode for instant meetings," "Waiting Room," and "Only authenticated users can join meetings" are enabled by default.
- Customize Chat Settings: Decide whether participants can save chats, or if private chats are allowed. Disabling private chat between participants can prevent out-of-band communication that might bypass host oversight.
- Manage User Roles and Permissions: If you manage a larger account (e.g., for an organization or school), properly assign user roles (e.g., host, co-host, alternative host) to delegate responsibilities without compromising overall security.
2. Educating Participants: The Human Element of Security
Technology alone cannot guarantee security. Human awareness and behavior play a significant role. Educate your participants on cyber security best practices for Zoom.
- Share Meeting Guidelines: Before the meeting, send out clear instructions on how participants should join, what security measures are in place (e.g., waiting room, muted upon entry), and expected conduct.
- Warn Against Sharing Sensitive Information: Remind participants not to share personal or sensitive information in the chat or verbally unless absolutely necessary.
- Report Suspicious Activity: Encourage participants to report any unusual or suspicious behavior to the host immediately.
3. Post-Meeting Best Practices
Security considerations don't end when the meeting does.
- Review Recordings: If you recorded the meeting, review the recording for any anomalies or unauthorized content before sharing or archiving.
- Delete Unnecessary Data: If local recordings or chat logs are no longer needed, delete them securely.
- Report Security Incidents: If a Zoom bombing incident or other security breach occurred, report it to Zoom (if applicable) and your organization's IT security team for analysis and future prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Zoom bombing and how can I prevent it?
Zoom bombing is the act of uninvited individuals gaining unauthorized access to a Zoom meeting and disrupting it, often with offensive content or harassment. You can prevent it by always using a strong meeting passcode, enabling the Waiting Room feature, disabling "Join Before Host," and restricting screen sharing security to "Host Only." Locking the meeting once all legitimate participants have joined is also highly effective.
Is Zoom's end-to-end encryption truly secure for sensitive conversations?
Zoom offers both standard encryption (AES 256-bit GCM, which is very robust for most uses) and true end-to-end encryption (E2EE). For highly sensitive conversations where E2EE is critical, you can enable it, but be aware that it disables certain features like cloud recording, live transcription, and polling. For the highest level of privacy, ensure all participants have E2EE enabled, understand its limitations, and verify its activation within the meeting settings.
How do I manage participants and remove disruptive individuals from my meeting?
As the host, you have full host controls. Access the "Participants" panel or the "Security" icon in your meeting toolbar. From there, you can "Remove" disruptive participants, who will then be unable to rejoin. You can also "Mute All" or restrict chat access. For extreme cases, the "Suspend Participant Activities" feature under the Security icon will halt all participant actions, allowing you to regain control.
What are the most critical Zoom settings to change immediately for better security?
The three most critical settings to enable or verify are: 1) Always require a passcode for your meetings; 2) Enable the Waiting Room feature for all meetings; and 3) Disable "Join Before Host." These foundational privacy settings significantly reduce the risk of uninvited guests and unauthorized access to your virtual sessions.

0 Komentar